
If your blog has more than one content writer or you want different members of your team to edit the site, you can decide their roles in running the site. This way you are able to assign them the permissions that are most appropriate to their responsibilities. Find out how to do this!
Roles in WordPress
A role in WordPress signifies which actions about a site a user can perform. Permissions range from the lowest, such as leaving a comment under a post, to the most advanced, such as modifying themes, plugins or granting permissions to additional users. WordPress allows you to specify the following roles (listing from the highest level of control over the site):
- Administrator
If you create a site in WordPress, by default your role is just Administrator. This means that you have full control over the site. You can perform all actions in it, including:
- edit and change theme,
- manage plugins,
- edit site code,
- add and remove users and change their permissions.
- Editor
An editor is a high-powered role that allows the editor to administer the site independently. However, an editor cannot make fundamental changes, which are within the highest powers of an administrator. Among other things, the editor’s privileges allow you to:
- creating, publishing, editing and deleting posts and pages,
- managing comments (moderation),
- publishing posts of other users,
- adding items to the Media Library and removing and inserting them into the content.
The task of the Editor is to exercise full control over the content created by users of lower ranks. The Editor also decides on the final shape of the materials and the time of their publication.
- Author
Authors’ rights allow them to control the content they create. Thus, they can, first of all:
- create, edit and delete your own entries,
- publish articles and delete them even after publication,
- add content to the media library and insert it into articles.
The fact that authors are also authorized to publish articles means that they do not have to go through the hands of an editor. This gives them a fair amount of autonomy, but also limits to some extent the site owners’ control over the quality of entries and the timing of their publication.
- Contributor
A contributor has lower powers than an author. The difference is that he or she cannot publish the posts he or she has created, which is the authority of an editor. So if you want to have full control over what content appears on the blog, assigning a user to this role will be a good choice. You will then retain the ability to decide, for example, the publication schedule and to check the posts you have created before posting them on the site.
- Subscriber
A subscriber has the lowest level of privileges to the site. He can only view other users’ posts, add comments and change his profile data. This role is most often used to allow visitors to receive newsletters. It also provides a chance to hide some content from unregistered users.
Assigning roles in WordPress
Assigning a role to a user is done when the user’s account is created. To do this, in the administration panel menu, select Users, and then Add New:
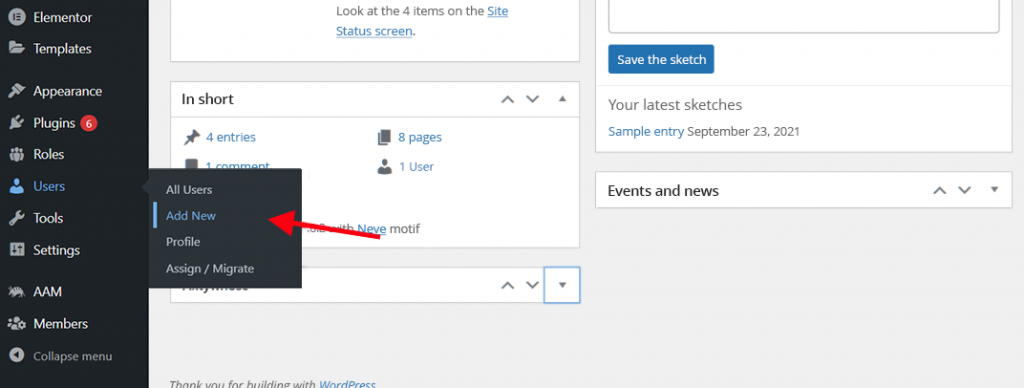
A screen will then appear that allows you to create a new user account, as well as select any permissions for it:
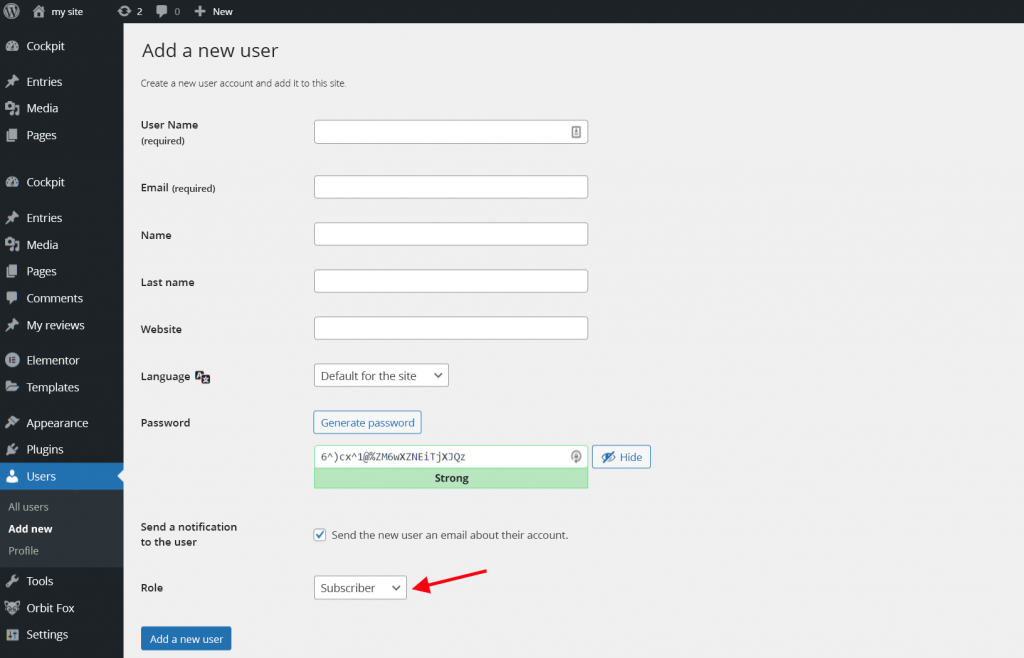
As an Administrator, you can edit assigned permissions through the All Users tab. By selecting a specific user, you will gain access to edit information about that user, and you will also have the ability to change their role.
Role management plugins
For some administrators, WordPress’ functionality when it comes to managing user permissions may not be enough. In this case, the solution is plugins that give access to more options. It is worth trying here especially:
Members is an advanced and popular plugin for managing roles in WordPress. It allows you not only to define users with standard permissions, but also to create new types of roles. This will decide any of their permissions.
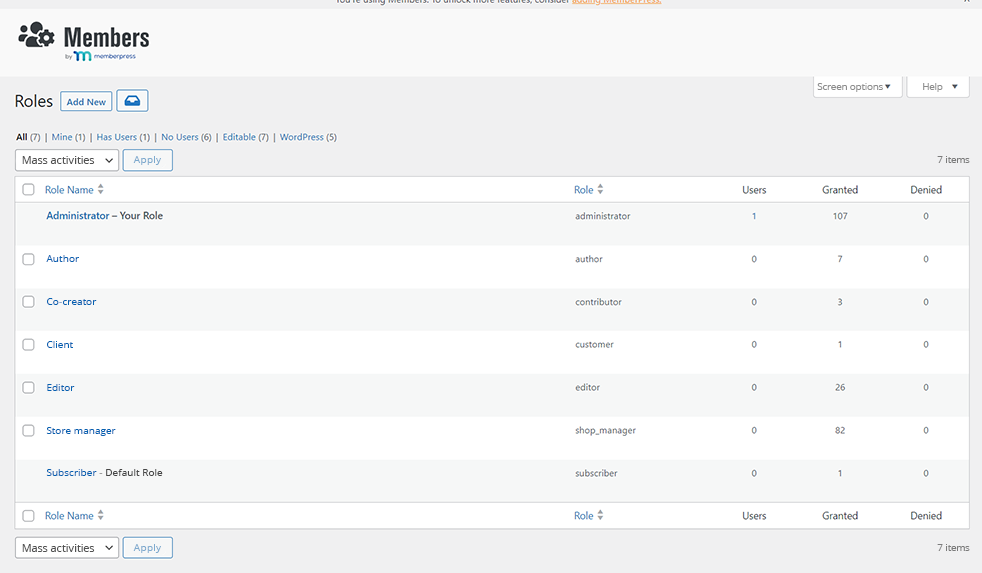
This is a very powerful plugin, which will give you the ability to create and manage custom user roles. You can also decide what elements of the admin panel each person can see. If you want, you will also create temporary user accounts, and by securing the login process, you will decide which elements of the site content they can see.
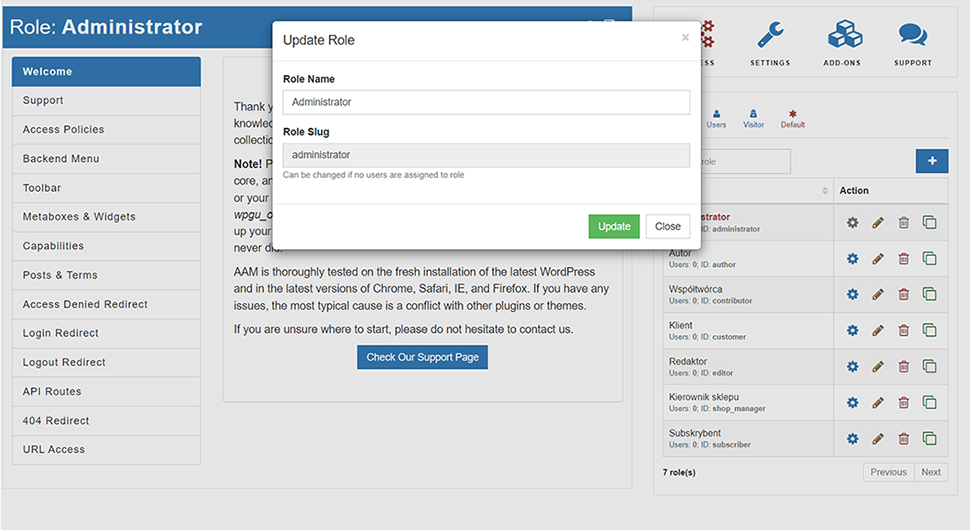
The advantage of this plug-in is not only its functionality, but also the easiest to use of the solutions mentioned. Among other things, it allows you to create roles with arbitrary names and permissions, as well as assign multiple roles to users.
Additional plug-ins give Administrators ample opportunities to manage user permissions on a site created in WordPress. At the same time, for most managers, the CMS’s basic functionality in this regard is completely sufficient. The use of custom roles, however, may make sense for sites with multiple contributors.
Hosting customized for WordPress
The WordPress CMS is appreciated by millions of webmasters around the world. To enjoy its full capabilities, it is worth running it in an optimized environment. CloudHosting WordPress from netart.com ensures a high level of security and high speed of websites based on this most popular content management system. It has integrated packages of modules specially selected for blogs, websites, online stores and galleries.
Each CloudHosting WordPress user gets access to the resources of 4 vCPUs (20 GHz) and 8 GB of RAM. Combined with LXC containerization, this makes sites run faster and more stable. The high speed of operation is also made possible by the use of powerful Intel Optane drives and Intel Xeon server processors, as well as the implementation of automatically configured Redis storage.